Table of Contents
In analysis of market structure, identification of valid pullback is crucial. It is because incorrect identification can lead to incorrect analysis. Pullback is simple retracement in its impulsive move. However, valid pullback takes multiple consideration. In ICT (Inner Circle Trader) trading, a valid pullback refers to a temporary price retracement within a larger trend, where traders look for opportunities to enter trades in the direction of the prevailing trend.
Understanding Pullback
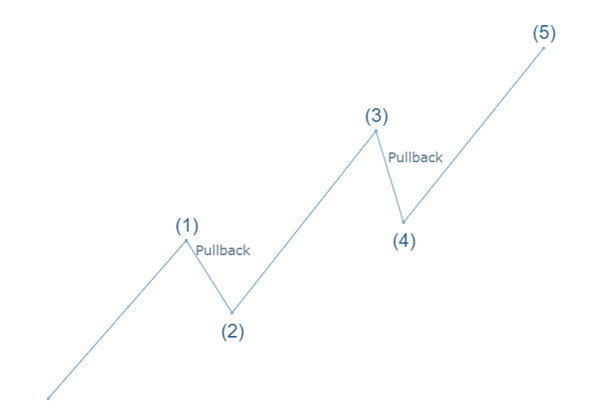
Market movement is fractal in nature. Market moves up with creating higher highs and higher lows, and moves down with creating lower highs and lower lows. Pullback on chart never indicate any kind on reversal. It is a retracement of an impulsive move. The following are the characteristics of a pullback:
- Pullback is temporary in nature. It is not considered as a trend reversal but a short-term counter-movement within the existing trend.
- It occurs in any market.
- Pullbacks are often seen as healthy corrections.
- Pullbacks often presents opportunities.
Pullbacks are a common feature of financial markets, and recognizing then can help us make more informed decisions about entering or exiting trades.
Valid Pullback In SMC
In general, pullback is referred to as a retracement of an impulsive move. The retracement can be with a single or with multiple candlesticks. In uptrend movement, bearish candlesticks are called pullbacks. In downtrend, bullish candlesticks are called pullbacks.
It is important to remember that pullback is a retracement move, but not all retracements are considered as valid pullbacks. In uptrend, a pullback candle must grab the low of the highest candle. In downtrend, a pullback candle must grab the high of the lowest candlestick.
Identification of Valid Pullback in Uptrend Market
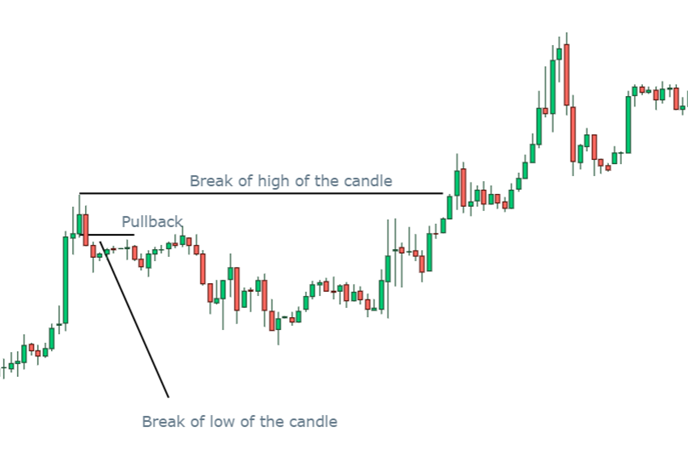
Identification of valid pullback in bullish market is not difficult task. It takes nothing but a careful analysis of candlestick patterns and price action. The following steps are included in identification of valid pullback:
- First step is to Identify the last highest bullish candlestick. The highest candle is significant because it represents the most recent peak in the bullish movement.
- After identification of the highest candle, the second step is to mark the low of the same candle. This low of the candle is a critical level for evaluating the validity of the pullback.
- Third step is the decisive one. During the pullback, observe whether the price goes below the low of the highest bullish candlestick. This can happen through a wick (where the price briefly dips below the low but closes above it) or through a full candlestick close below the low. The “grabbing” of this low is crucial because it may indicate that the market is testing the strength of this level and hunting for liquidity.
- When the low has been grabbed, the next step is to see if the price breaks above the high of the highest bullish candlestick. This break above the high signifies that the bullish momentum has resumed and the pullback is likely over. It confirms that the market has absorbed the selling pressure during the pullback and is now continuing in the direction of the original uptrend.
This is the general criteria for identification of a valid pullback. A real market example is given below:
Other than the pullback, the most satisfying thing in the chart is that market grabbed the low of the strongest bullish candlestick. It is because not all, especially ICT traders, consider SMC pullback a valuable trading strategy. They rather prefer a strong corrective phase (pullback to premium and discount zone) before continuation of the trend.
Identification of Valid Pullback in Downtrend Market
Identification of valid pullback in bearish market is not difficult task. It takes nothing but a careful analysis of candlestick patterns and price action. The following steps are included in identification of valid pullback:
- Our first step is to identify and locate the lowest bearish candlestick before the market begins to pullback. This represents most recent point of significant down move.
- After identification of the last bearish candlestick, mark the high of the candle. This high serves as a crucial level for accessing the validity of the pullback.
- During the pullback (i.e., during the formation of bullish candles), observe whether the price goes above the high of the lowest bearish candlestick. This could happen through a wick (where the price briefly touches or slightly exceeds the high but closes below it) or through a full candlestick close above the high. The “grabbing” of this high is critical because it may indicate that the market is testing the strength of this level, possibly hunting for liquidity.
- After the high has been grabbed, the next step is to see if the price drops below the low of the lowest bearish candlestick. This break below the low signals that the bearish momentum has resumed and the pullback is likely over. It confirms that the market has absorbed the buying pressure during the pullback and is now continuing in the direction of the original downtrend.
This is the general criteria for identification of pullback in bearish trend. Real market example is given below:
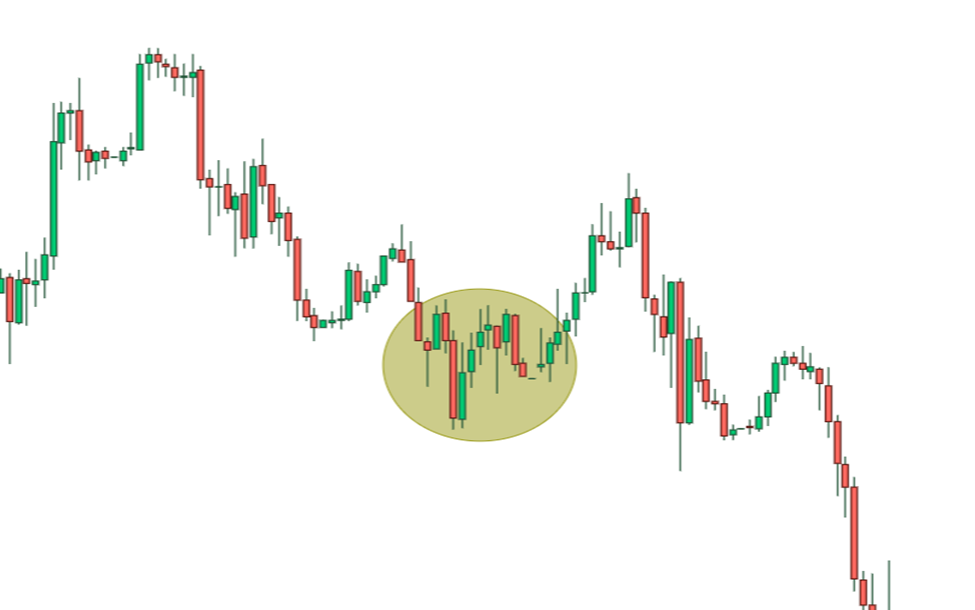
Here, in circle, you can observe that more than one candle breaks the high of the last bearish candlestick. Pullback can take place with multiple candlesticks.
Final Thought
In trading, identifying valid pullbacks—whether in bullish or bearish markets—requires careful analysis of candlestick patterns, price action, and key levels. This method helps traders optimize entry points and manage risk. However, all trading involves risk, and past performance does not guarantee future results. Always conduct thorough research, use proper risk management strategies, and be prepared for potential losses.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is a pullback in trading?
A pullback is a temporary decline or reversal in the price of an asset within a prevailing trend. In an uptrend, it’s a short-term dip, while in a downtrend, it’s a brief rise.
How to identify a valid pullback in a bullish market?
Look for the highest bullish candlestick before the pullback, mark its low, check if the pullback candlesticks dip below this low, and then ensure the high of the candlestick is broken.
What is the significance of marking the highest bullish or lowest bearish candlestick?
Marking these candlesticks helps determine key levels of support and resistance. It allows you to assess whether the pullback is merely a temporary retracement or indicative of a trend reversal.
What are common mistakes to avoid when trading pullbacks?
Avoid entering trades too early, relying solely on one indicator, or neglecting overall market context. Ensure you confirm the pullback with multiple signals and maintain discipline in your trading strategy.
I’m Abdullah Shah, a content writer with three years of experience in crafting engaging and informative content. My background in market analysis complements my work, allowing me to create content that resonates with audiences. I’m also a seasoned practitioner in the forex and crypto markets, with a strong foundation and deep interest in finance. My passion for the financial world drives me to produce content that is both insightful and valuable for those interested in understanding market trends and financial strategies.