Table of Contents
ICT traders focus on each and every move of the market. Fair Value Gap (FVG) arise in the forex market when rapid price movements create gaps between candles, signaling an imbalance between supply and demand. These gaps highlight areas where the market has not achieved equilibrium, often due to a sudden influx of buying or selling pressure. ICT and Smart Money traders use FVGs to identify potential retracement points where price might return before continuing its trend, making them valuable tools for spotting high-probability trade entries within the broader context of market dynamics.
Understanding Fair Value Gaps in Trading
Fair Value Gaps (FVGs) in trading occur when rapid price movements leave unfilled gaps between candles, highlighting areas where the market didn’t trade. These gaps represent a lack of liquidity, typically caused by strong buying or selling pressure. In market dynamics, such imbalances suggest that price moved too quickly, bypassing certain price levels, which often signals an inefficiency in the market.
Market participants watch for these FVGs because price often retraces to these gaps, seeking to fill them and balance liquidity. This retracement is part of the market’s natural tendency towards efficiency, as it revisits these untraded zones to ensure all price levels are effectively covered. For ICT and SMC traders, identifying Fair Value Gaps can offer strategic entry points, anticipating a return to these gaps before the market resumes its original direction.
Fair Value Gaps are particularly powerful when combined with other market analysis tools, such as support and resistance levels or order blocks. In the context of a broader market trend, FVGs can indicate either a continuation or a potential reversal, depending on where they appear in the price structure. Understanding these dynamics helps traders make informed decisions, leveraging FVGs to enhance their trading strategies.
Identification of Fair Value Gap (FVG)
FVGs are formed because of displacement in price. Fair Value Gaps are also known as imbalances in price movement. This happens in the market because there is very little participation and path of least resistance is clear for institutions and “Big Money”. They take advantage of the situation and move price in one direction. Fair Value Gaps are identified on candlestick charts in the following way:
- In identifying FVGs, three candlestick structure is formed in the market. The middle candle serves as the key candle used in identification of Fair value gap. At the same time, the first and third candles helps define the gap’s boundaries.
- ICT trader focuses on the relationship between the first and third candle. In an uptrend, if the low of the third candle is higher than the high of the first candle, and the middle candle doesn’t overlap with the first, an FVG has formed. In a downtrend, if the high of the third candle is lower than the low of the first candle, it indicates a gap.
Its significance and importance is linked with overall market structure and trend context. Order Blocks near the FVG is considered as the important one. If FVG is in harmony with a broader trend or a key level, it becomes a reliable signal for continuation of a trend.
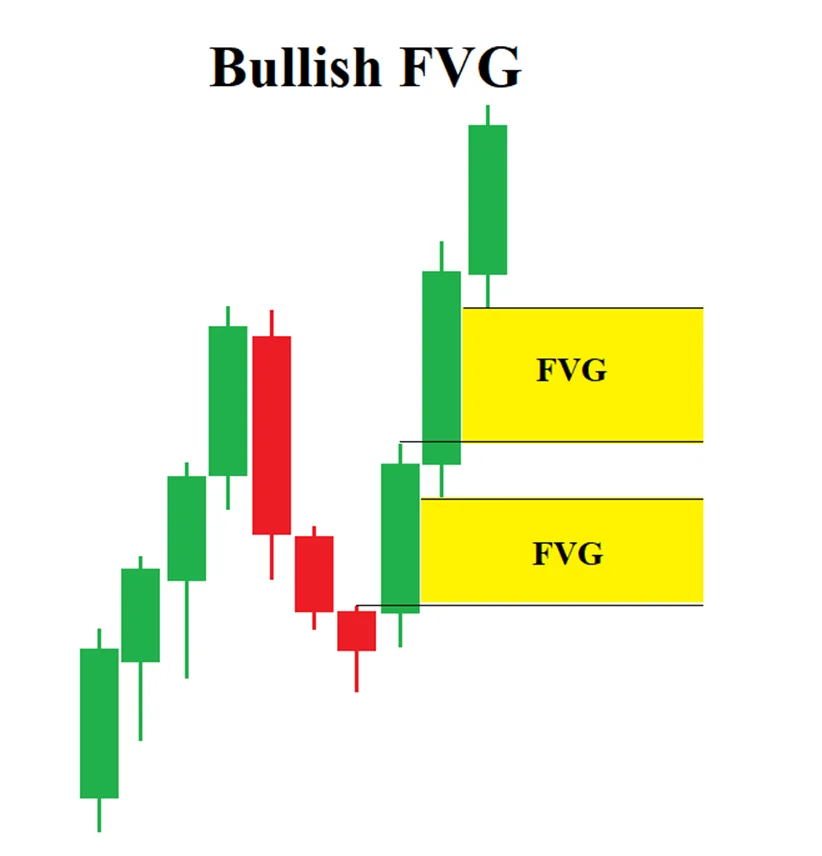
Bullish ICT Fair Value Gap
In ICT trading concepts, Fair value gap is an area where there is a notable between candles. In uptrend, FVGs are temporary imbalance in the market. It indicates strong buying pressure by Institutions and market maker.
- The first candle in the sequence.
- The middle candle, which causes the gap. It typically has a large bullish body, with the price opening higher and closing even higher, reflecting strong upward momentum.
- The third candle, which doesn’t fully overlap with the first candle, leaving a gap.
This is the general criteria that every FVG in bullish trend. The low of the third candle must be higher than the high of first candle. The gap between first candle high and third candle low is the bullish FVG. In this area, market move too quickly and denotes aggressive buying in that area.
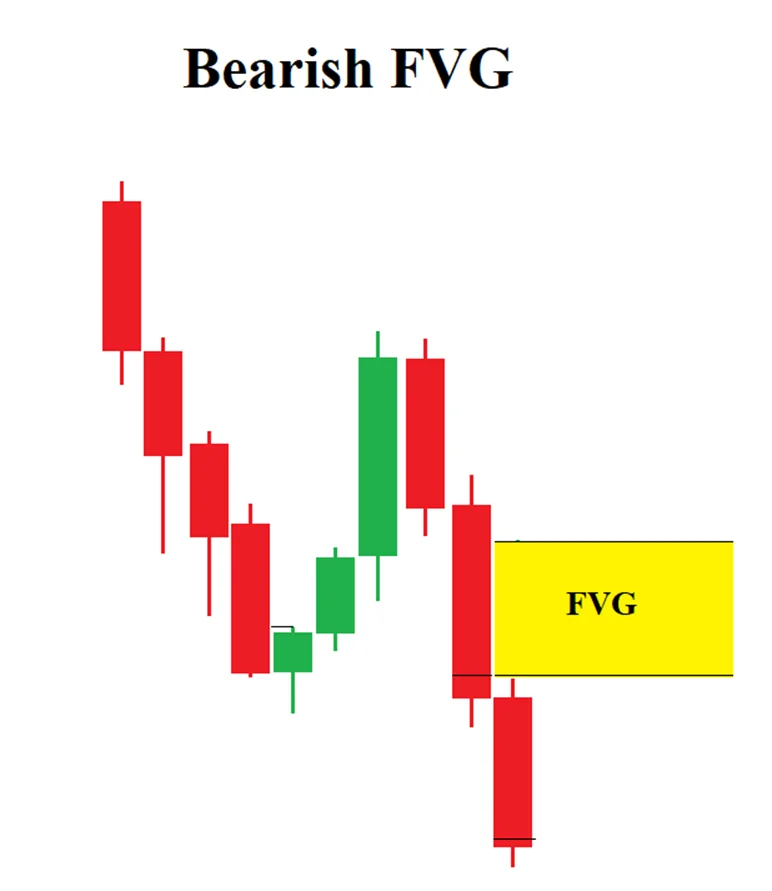
Bearish ICT Fair Value Gap (FVG)
In downtrend, FVGs are temporary imbalance in the market. It indicates strong selling pressure by Institutions and market maker.
- The first candle in the sequence.
- The middle candle, which causes the gap. It typically has a large bearish body, with the price opening lower and closing even lower, reflecting strong downward momentum.
- The third candle, which doesn’t fully overlap with the first candle, leaving a gap.
This is the general criteria that every FVG fulfill in bearish trend. The high of the third candle must be lower than the low of first candle. The gap between first candle high and third candle low is the bearish FVG. In this area, market move too quickly and denotes aggressive selling in that area.
Use of FVG in Trading
Just like not all formations of candlestick patterns are valid on chart, same applies to Fair Value Gaps. Correct use of FVG in trading require understanding of prior trend and market structure.
In an uptrend, price of an asset may eventually retrace to fill the bullish FVG as the market seeks to rebalance liquidity. ICT traders see this retracement to the FVG as potential buying opportunity. They thought that market may use the area to gather more order before continuing its trend.
In a downtrend, price of an asset may eventually retrace to fill the bearish FVG as the market seeks to rebalance liquidity. ICT traders see this retracement to the FVG as potential selling opportunity.
Bullish and Bearish FVGs are significant only when aligned with other bullish and bearish signals. Proper break of structure and retracement to the level is crucial. If FVG appear near supply or demand zone, it increases its authenticity.
Examples of Fair Value Gap
In market, Bullish FVG appears just like the example below.

After creating imbalances, market retrace to fill the imbalance. Market often tries to reach Equilibrium level before continuing its upward trend.
In downtrend market, Bearish FVG appears just like the example below.
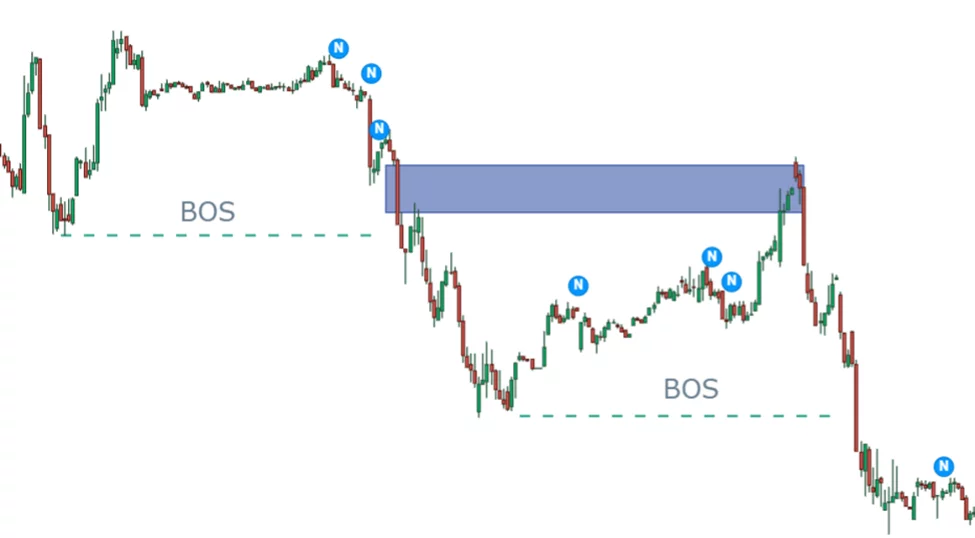
Market retraces to fill the imbalances. ICT traders find further signal when the market reaches the imbalance area. It is necessary to draw premium and discount. Premium zone in downtrend helps to filter selling opportunities and avoid inducements. It is advised to take trades on first pullback, it is often inducement laid down by institutions.
Final Note
Fair Value Gaps (FVGs) are powerful tools within the ICT framework for identifying potential market retracements and trade setups. However, trading involves significant risks, and no strategy guarantees success. It is crucial to combine FVGs with other analysis techniques. Always use stop-loss orders, and only risk capital you can afford to lose. Continuous learning and discipline are key to long-term trading success.
FAQs
What is a Fair Value Gap (FVG)?
A Fair Value Gap (FVG) is an area on a price chart where there is a gap between candles. It indicates an imbalance in the market due to rapid price movement. It represents untraded price levels caused by strong buying or selling pressure.
How to Identify Bullish FVG?
A Bullish FVG appears in an uptrend when the low of the third candle is higher than the high of the first candle, leaving a gap. This gap often serves as a potential area for price retracement before continuing upward.
How to identify a Bearish FVG?
A Bearish FVG appears in a downtrend when the high of the third candle is lower than the low of the first candle, leaving a gap. This gap may act as a retracement zone before the price continues its downward movement.
Can FVGs guarantee a successful trade?
FVG or any other ICT tools never guarantees a success in trading. However, they are used in conjunction with other ICT tools like market structure, order blocks, and risk management to improve success ratio in trading.
I’m Abdullah Shah, a content writer with three years of experience in crafting engaging and informative content. My background in market analysis complements my work, allowing me to create content that resonates with audiences. I’m also a seasoned practitioner in the forex and crypto markets, with a strong foundation and deep interest in finance. My passion for the financial world drives me to produce content that is both insightful and valuable for those interested in understanding market trends and financial strategies.