Table of Contents
Market is a constant competition between buyers and seller. Each side tries to push price in their favor. At the end, those who have an edge over their competitor takes the price in their favorable direction. They get the fuel of the market. This fuel in financial market is known as Liquidity. Liquidity in market refers to the pending orders needed to be executed. Liquidity is broad concept in financial markets. A specific concept within liquidity is Liquidity Sweep.
SMC and ICT traders use such concepts within a price range to look for potential opportunities. This article explores its importance in understanding underlying market dynamics and price movements, and provides detailed analysis of Liquidity sweeps.
Understanding Liquidity and Liquidity Sweep
Understanding the concepts of liquidity is crucial for understanding concept of “Liquidity Sweep”. In trading market context, liquidity refers to how easily an asset can be bought or sold without significantly affecting its price.
Liquidity, in more concrete terms, refers to pending orders in the market. The pending orders needed to be executed by market participants. There is other form of pending orders which are known as stop-loss orders. Institution may manipulate the price on specific points to gather more assets before continuing the price in their favor.
In financial markets, High liquidity means that there are more enough buyers and seller for transaction to occur smoothly and at stable prices. On the other hand, low liquidity implies that executing large trade may cause substantial price fluctuations.
Liquidity sweep in financial markets occurs when large market participants, especially institutions and market makers aggressively trade on one side of the order book. The aggressive action of market participants sweeps the available orders from the market and drive the price up or down.
ICT Liquidity Sweeps
ICT traders often look for liquidity sweep in the market. Liquidity sweep in market are major area where market seeks liquidity before making a significant reversal. Liquidity refers to the order and stoploss waiting to be executed. The buys and sell order are placed at areas above and below key levels like equal highs and equal lows, or previous swing points.
These areas serve as liquidity pools where retail traders often place stop-losses or breakout orders. In liquidity sweep, price movement is intentionally directed toward these liquidity zones to trigger these orders.
In an uptrend, price forms equal highs or lows, the break of price above and below is considered as trading opportunity on that side. Their buy-stop orders create a pool of buy-side liquidity. Market makers often push the price slightly above these equal highs to trigger the buy orders, then immediately reverse the price with strong selling pressure. That is just one situation. However, mostly equal lows are swept by institutions. This rapid reversal catches retail traders off guard, trapping them in losing positions.
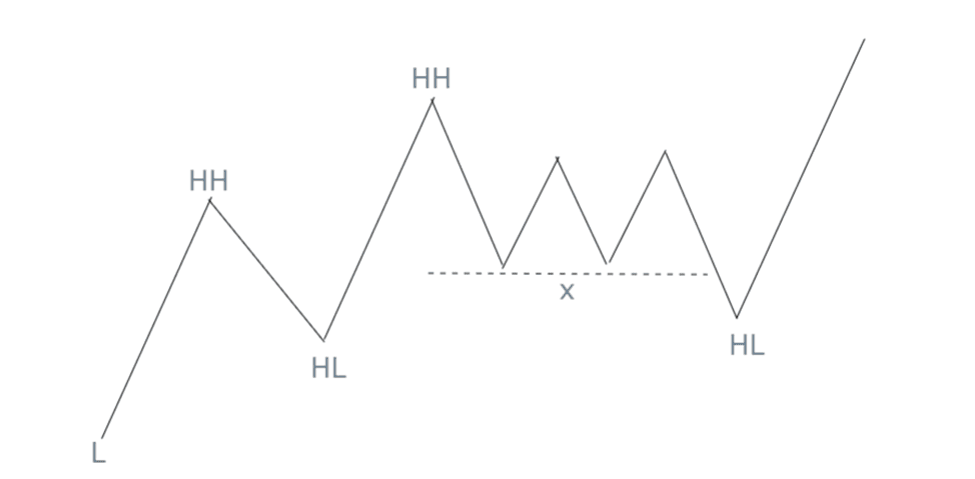
The sweep occurs when the price temporarily breaches a significant level, like the equal highs, but fails to sustain above it, signaling a false breakout. If the price closes above the highs but quickly reverses with heavy selling momentum, it confirms that the move was primarily to capture liquidity rather than continue the upward trend. Similarly, liquidity sweeps can occur to the downside when price targets equal lows or prior swing lows to capture sell-side liquidity before reversing upward.
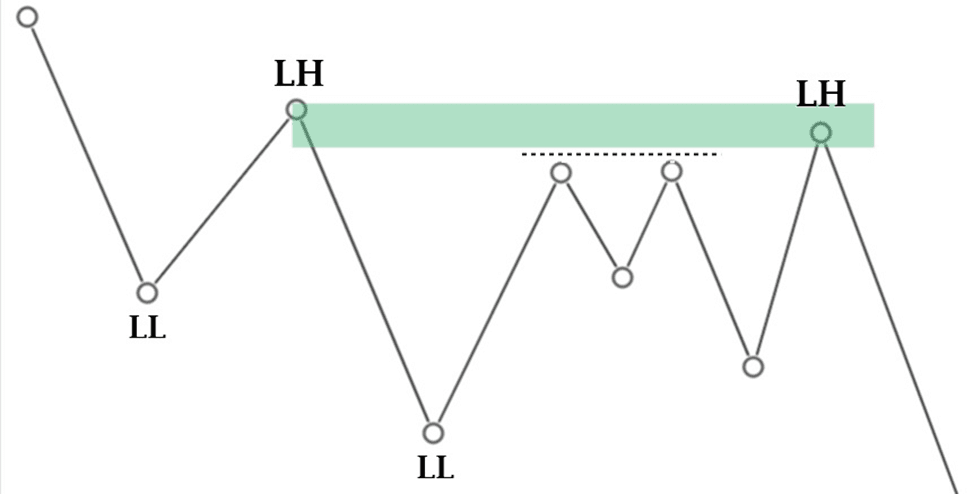
This is the scenario takes place within ICT dealing Range. Sometime, liquidity sweeps occur within major market structure. Market sweeps the liquidity above swing high and then retraces and continue its prior trend. On the other hand, market sweeps the liquidity below the swing low and then retraces and continue its trend.
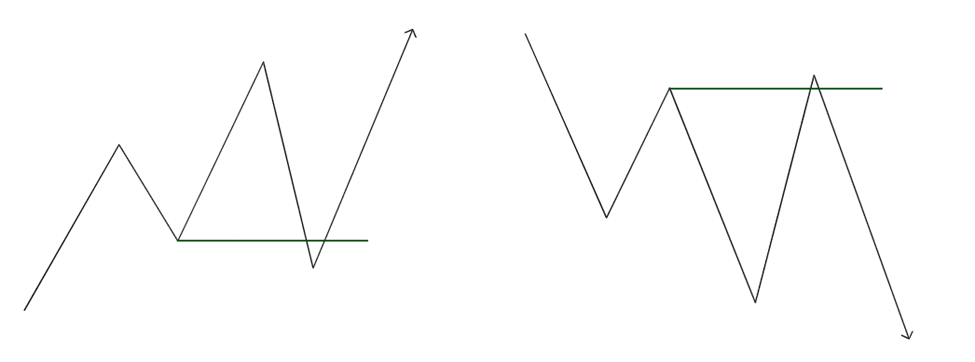
Anticipating Liquidity Sweep in Bullish Market
In Market Structure Analysis, we usually mark ICT dealing range. In Bullish Market structure, we expect price to test PD array in Discount area. Smart money and ICT trader look for specific type of behavior.
In Bullish Market, institutional traders aims to buy at lower prices and sell at higher prices. That could be the reason when market collects buy side liquidity, they drive the price lower in order to accumulate assets and expect higher prices in future. SMC and ICT traders wait for the price to pullback to the discount area (50% of the ICT Dealing Range). In the discount areas price often respect PD array. PD Array refers to key price levels like Order Blocks, Fair Value Gaps, or Imbalances zone. These zones are considered as attractive zone for entering buy positions.
Price often creates often compelling structure within ICT Dealing Range. The structure can be consolidation range or equal high or lows. In consolidation market, there is liquidity on both side of the market and institutions capture the liquidity for their purposes. Equal highs or lows capture their attention.
Other possible scenario for liquidity sweep in Bullish Market is that market often sweep sell side liquidity. SMC and ICT trader see swing low as prime target for liquidity. The market may drive price below these swing lows and trigger retail stop-losses.
Anticipating Liquidity Sweep in Bearish Market
In Market Structure Analysis, we usually mark ICT dealing range. In Bearish Market structure, we expect price to test PD array in Premium area. Smart money and ICT trader look for specific type of behavior.
In Bearish Market, institutional traders aim to sell at higher prices and buy at lower prices. That could be the reason when market collects sell side liquidity, they drive the price higher in order to accumulate sell orders and expect lower prices in future. SMC and ICT traders wait for the price to pullback to the premium area (50% of the ICT Dealing Range). In the premium areas price often respect PD array. PD Array refers to key price levels like Order Blocks, Fair Value Gaps, or Imbalances zone. These zones are considered as attractive zone for entering sell positions.
Price often creates compelling structure within ICT Dealing Range. The structure can be consolidation range or equal high or lows. In consolidation market, there is liquidity on both side of the market. Institutions capture the liquidity for their purposes. Equal highs or lows capture their attention.
Other possible scenario for liquidity sweep in Bearish Market is that market often sweep buy side liquidity. SMC and ICT traders see swing high as prime target for liquidity. The market may drive price above these swing highs and trigger retail stop-losses.
Final Note
Liquidity sweeps are a powerful tool for identifying potential reversals and trapping retail traders. By understanding how the market targets liquidity pools, such as equal highs or lows, traders can align their strategies with smart money movements. However, liquidity sweeps are not foolproof and should be used alongside proper risk management and other technical analysis tools.
Trading liquidity sweeps involves significant risk, as market conditions can change unexpectedly. Traders must always set stop-losses and manage position sizes carefully. Losses can exceed initial investments, so it’s essential to trade within your risk tolerance and use liquidity sweeps wisely.
FAQs
What is a Liquidity Sweep?
A liquidity sweep is a market move where price briefly surpasses a key level, such as equal highs or lows, to trigger stop-loss orders or breakout trades before reversing in the opposite direction. It occurs when the market seeks liquidity from retail traders before continuing or reversing a trend.
How Does a Liquidity Sweep Work?
In a liquidity sweep, price targets areas with a high concentration of stop-loss orders or pending trades. Once liquidity is captured, often through a temporary break of a support or resistance level, the market reverses as smart money or institutional traders enter their positions.
What is the Role of Liquidity Sweeps in Institutional Trading?
Institutional traders use liquidity sweeps to enter positions at advantageous prices. By forcing the market to sweep liquidity, they trigger retail orders and gain access to the liquidity needed to execute large trades without significant slippage.

I’m Aatiq Shah, a dedicated forex and crypto market practitioner with three years of hands-on experience. Currently, I’m working as a Financial Manager. My journey in the world of finance has equipped me with the skills and knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of the forex and crypto markets.